You’re sitting in the eye doctor’s chair, lights dim, air a little chilly, and the optometrist leans in. A few drops land on your eye, cool at first, then strangely tingly. “Your pupils will dilate in a few minutes,” they say with a reassuring smile. You nod, but you already know what’s coming. Your world is about to get weirdly bright, text will look like it’s shouting at you, and your pupils will resemble a cat at midnight.
But the real question people ask sometimes quietly, sometimes desperately, is:
How long does eye dilation actually last?
And beneath that lies an even deeper curiosity:
Why does it take so long? Why do some people recover quickly while others spend half the day squinting like they’re staring into the sun?
This article answers every question you’ve had (and the ones you never knew to ask). Think of it as the ultimate guide to science, history, expert insights, real cases, modern research, and future predictions rolled into one.
Let’s begin.
What Actually Happens When Your Eyes Dilate? (A Quick, Fascinating Primer)
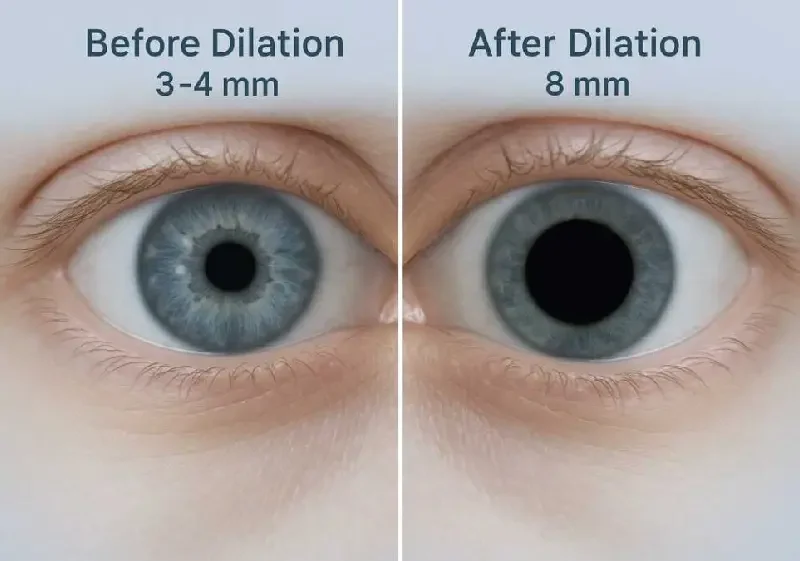
Before we talk timelines, you need a simple visual. Your pupil is like the lens opening on a camera. It expands and contracts depending on light.
Dilation drops force your pupil to stay wide open, giving doctors a full view of your retina, optic nerve, and the inner workings of your eye.
But here’s the interesting part:
Your pupil muscles aren’t passive. They’re responsive, quick, and reactive—until dilation drops override them.
Think of it as a temporary off-switch.
And like any system that’s switched off chemically, it takes time to power back on.
How Long Does Eye Dilation Last? (The Quick Answer)
For most adults, dilation lasts:
4–6 hours on average
But depending on the drops used, your age, eye color, and health, the effects may last:
As short as 2 hours
As long as 24 hours
In children, dilation can last even longer—sometimes up to 36 hours.
Sounds like a big range? It is. And here’s why.
The Real Factors That Determine How Long Eye Dilation Lasts
1. Type of Dilation Drops Used (The #1 Factor)
You might not realize it, but different dilation drops have wildly different half-lives.
Below is a simple breakdown.
Common Dilation Drops & Their Duration
| Drop Name | Purpose | Typical Duration | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tropicamide (1%) | Standard eye exams | 4–6 hours | Most commonly used |
| Phenylephrine (2.5%) | Wider dilation for retinal view | 2–4 hours | Often used with tropicamide |
| Cyclopentolate | Children, focusing on tests | 8–24 hours | Strong effect |
| Atropine | Amblyopia therapy | 24–72 hours | Very long-lasting |
If your doctor used tropicamide, expect the shortest experience.
If your child was given cyclopentolate or atropine, clear your schedule.
Key Takeaway
The stronger the medication, the longer the dilation lasts—sometimes exponentially longer.
Age Matters More Than People Realize
Children’s eyes respond differently. Their focusing muscles are stronger, more flexible, and more resistant. So doctors use stronger drops.
Typical Duration by Age
| Age Group | How Long Does Dilation Last |
|---|---|
| Adults | 4–8 hours |
| Teens | 6–12 hours |
| Young Children | 12–24 hours |
| Babies | 24–36 hours |
Why longer in kids?
Their ciliary muscles (the focusing muscles) bounce back more slowly from medication.
Eye Color Influences Dilation Duration (Really!)
This surprises most people.
Melanin, the pigment that gives your eyes color, also absorbs medication.
That means:
-
Light eyes (blue, green, hazel) → Drops work faster, wear off sooner
-
Dark eyes (brown, black) → More melanin absorbs medication → Effects last longer
Average Duration Based on Eye Color
| Eye Color | Duration |
|---|---|
| Light | 3–6 hours |
| Medium | 4–8 hours |
| Dark | 6–12 hours |
This is one of the most consistent real-world patterns doctors observe.
Metabolism & Health Conditions
Your body chemistry matters.
People who metabolize drugs faster (common in young adults and athletes) often recover quickly.
But some conditions can prolong dilation:
-
Diabetes
-
Neurological disorders
-
High myopia
-
Medications like antihistamines or antidepressants
Key Takeaway
Your eyes don’t function in isolation. Your entire body affects recovery.
First-Time Dilations Last Longer (Case Study)
A 37-year-old patient reported that her first dilation lasted nearly 8 hours, while subsequent dilations typically wore off in just 4–5 hours.
Doctors confirm this pattern. Your eyes become familiar with how these drops work, so future dilations can feel milder and shorter.
A Brief History of Eye Dilation (And Why It Hasn’t Changed Much)
Ancient Rome: The Cosmetics of Danger
Roman women used belladonna, a highly toxic plant, to dilate their pupils. They believed large pupils made them look more beautiful.
Ironically, belladonna means “beautiful woman.”
But its side effects could be deadly.
1800s: Dilation Enters Medicine
Ophthalmologists realized dilated pupils gave them a clear view of the retina. Dilation moved from cosmetics to medical practice.
1901: Tropicamide Is Born
Scientists introduced safer, shorter-acting dilation drugs. Tropicamide quickly became the standard.
Today: Same Purpose, Better Safety
Modern dilation drops aren’t perfect, but they’re precise, predictable, and safe. The core method hasn’t evolved because it simply works.
The Future of Eye Dilation (Yes, It’s Changing)
Researchers are developing:
-
Reversal drops that shorten the dilation time
-
Smart light-based imaging that reduces the need for dilation
-
AI retinal scanners that see through small pupils
-
Nanotechnology-based dilation mists (experimental)
Imagine a world where dilation takes 60 seconds—without blur or sensitivity.
We’re closer than you think.
What Does Eye Dilation Feel Like? (Real Experiences)
Most people describe dilation as:
-
Blurry near vision
-
Extra-sensitive to light
-
Slight pressure or heaviness
-
Strange glare halos
-
Difficulty reading screens or small text
But no pain.
If there’s pain, it’s not from dilation—it’s a separate issue.
Story Snapshot:
A software engineer once said:
“Dilation felt like someone turned the contrast to 200%. Beautiful but annoying.”
How to Make Eye Dilation Wear Off Faster (Scientifically Explained)
Strict truth:
You cannot instantly reverse dilation.
BUT you can reduce the discomfort.
Here’s how.
1. Wear sunglasses indoors and outdoors
Light sensitivity drops dramatically.
2. Use blue-light blocking glasses
Reduces glare from screens.
3. Avoid near work
Reading forces your ciliary muscles to work while they’re medically “turned off.”
4. Stay in soft lighting
Harsh lighting prolongs discomfort.
5. If you must read, increase text size
Your eyes won’t need to strain.
6. Use lubricating eye drops
Helps with dryness that occurs after dilation.
7. Don’t drive until you feel safe
Legal in many places, but not recommended if your vision is still blurred.
When Should You Worry? (Rare but Important)
Seek medical help if:
-
Dilation lasts longer than 24 hours (for adults)
-
You feel eye pain
-
You notice flashing lights
-
Your vision becomes foggy rather than just blurry
-
Only one pupil dilates during drop use
These are rare, but awareness keeps you safe.
Can You Go Back to Work After Dilation?
For Screen-Based Jobs:
You may struggle for 3–6 hours.
For Outdoor Jobs:
Wear dark sunglasses and take breaks.
For Driving Jobs:
Avoid driving until your vision fully returns.
Key Advice:
Don’t commit to important reading-heavy tasks the same day.
A Practical, Step-by-Step Guide: What to Do Before and After Dilation
Before Your Appointment
-
Bring sunglasses
-
Avoid driving yourself
-
Reduce screen time beforehand
-
Keep your schedule light
-
Stay hydrated
During the Exam
-
Ask which drops are being used
-
Blink often after the drops go in
-
Relax—dilation isn’t harmful
After the Exam
-
Put on sunglasses right away
-
Avoid bright sunlight
-
Increase screen/text size
-
Stay indoors if possible
-
Don’t rub your eyes
-
Wait for your vision to normalize before driving
Eye Dilation Pros & Cons (Simple Table)
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Detects early eye diseases | Temporary blurry vision |
| Helps diagnose retinal issues | Light sensitivity |
| Essential for diabetic checks | Inconvenient for work |
| Non-invasive & safe | Reading difficulty |
Key Takeaway:
The benefits far outweigh temporary discomfort.
FAQs
1. How long does eye dilation last on average?
Most people experience dilation for 4–6 hours, but it can last longer depending on the drops used.
2. Can dilation last 24 hours?
Yes, especially in children or when strong drops like cyclopentolate or atropine are used.
3. Do blue eyes dilate longer?
No—light eyes usually recover faster. Dark eyes may stay dilated longer.
4. Can I drive after dilation?
You shouldn’t drive until your vision feels fully normal.
5. How can I make dilation go away faster?
You can’t speed up the biology, but sunglasses, avoiding bright light, and reducing near work help you feel better.
6. Is dilation dangerous?
No. Serious complications are extremely rare.
7. Why do kids stay dilated longer?
Their focusing muscles are stronger, so doctors use more powerful drops.
8. Can I work on a computer after dilation?
Yes, but it may be difficult for 3–4 hours, depending on blur and light sensitivity.
9. Does dilation affect long-distance vision?
It mostly affects near vision, though brightness may impact long-distance clarity too.
10. Is dilation necessary every year?
For most adults—yes. Especially if you have risk factors like diabetes, high myopia, or a family history of eye disease.
Final Conclusion
Eye dilation usually lasts 4–6 hours, but it can range from 2 to 24 hours depending on the drops used, your eye color, age, and metabolism.
It might feel inconvenient, but it’s one of the most powerful, non-invasive tools for protecting your vision. Think of dilation like a temporary inconvenience that protects the windows to your world.
Your eyes are worth the time.