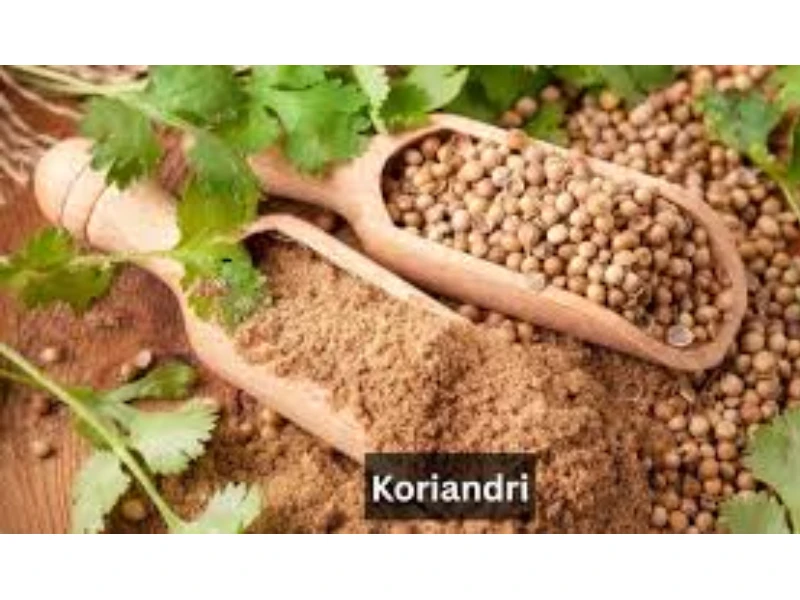
Koriandri, also known as coriander, is one of the most versatile herbs used worldwide. From aromatic leaves to flavorful seeds, it enriches cuisines, supports health, and has a fascinating history that dates back thousands of years. Whether you sprinkle fresh koriandri leaves over a salad, grind the seeds into spices, or explore its medicinal benefits, this herb has something for everyone. In this guide, we’ll explore everything about koriandri—from its origins and health advantages to cooking tips, growing methods, and safety precautions.
What is Koriandri? Understanding This Herb
Origin and History of Koriandri
Koriandri traces its roots to the Mediterranean region and parts of Western Asia. Historical evidence shows it was used in ancient Egypt for embalming and culinary purposes. In India, coriander has been a staple in Ayurveda for centuries, while in Mexico, the fresh leaves—commonly called cilantro—play a central role in salsas and garnishes. Over time, koriandri became a global herb, featured in Middle Eastern, European, and Asian cuisines. Its widespread use highlights its flavor, aroma, and medicinal value.
Parts of the Koriandri Plant
Koriandri is a multi-purpose herb, with different parts used for culinary and medicinal purposes:
-
Leaves (Cilantro): Bright green, aromatic, and slightly citrusy, the leaves are often used fresh to garnish soups, salads, curries, and sauces.
-
Seeds (Coriander Seeds): These are small, round, and brownish-yellow, with a warm, nutty flavor. They can be used whole, crushed, or ground into spice blends.
-
Roots: Less common but highly valued in Southeast Asian dishes, adding depth to curries, soups, and sauces.
Nutritional Profile of Koriandri
Koriandri is not just flavorful—it’s a nutritional powerhouse. Here’s a comparison of leaves and seeds:
| Nutrient | Koriandri Leaves (per 100g) | Koriandri Seeds (per 100g) |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | 23 | 298 |
| Protein | 2.1g | 12.4g |
| Vitamin C | 27mg | 21mg |
| Vitamin K | 310µg | 0µg |
| Iron | 1.8mg | 16.3mg |
| Calcium | 67mg | 709mg |
| Fiber | 2.8g | 41.9g |
| Antioxidants | High | Moderate |
Both leaves and seeds are rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals, supporting overall health in multiple ways.
Health Benefits of Koriandri
Koriandri is more than a culinary delight. Its compounds offer several health benefits:
Digestive Health
Koriandri stimulates digestive enzymes, easing bloating and indigestion. Adding fresh leaves to salads or drinking coriander seed tea can promote gut health. Think of it as a gentle cleanser for your stomach, improving nutrient absorption and preventing discomfort.
Anti-inflammatory and Antioxidant Properties
Koriandri contains polyphenols and flavonoids that combat inflammation and oxidative stress. Regular use may help reduce inflammation-related conditions like arthritis, while antioxidants neutralize harmful free radicals, supporting overall immunity.
Heart Health and Cholesterol Management
Several studies indicate that koriandri can help lower bad cholesterol (LDL) and triglycerides while increasing good cholesterol (HDL). Incorporating ground koriandri seeds into your diet can support cardiovascular health naturally.
Blood Sugar Regulation
Koriandri seeds have compounds that may help regulate blood sugar levels, making them a supportive food for individuals with diabetes. Drinking coriander seed tea or adding the ground seeds to meals can stabilize glucose spikes.
Skin and Detox Benefits
Coriander leaves have mild detoxifying properties. They help flush out toxins, support liver function, and promote healthy, glowing skin. Many traditional remedies use fresh leaves in face packs and tonics to reduce acne and blemishes naturally.
Culinary Uses of
Koriandri is as versatile in the kitchen as it is in medicine.
Using Koriandri Leaves (Cilantro) in Recipes
Fresh coriander leaves brighten the flavor of salads, soups, curries, and salsas. They’re usually added at the end of cooking to preserve aroma. For instance:
-
Sprinkle chopped leaves on guacamole or chutneys.
-
Mix into yogurt-based sauces for a fresh twist.
Cooking with Koriandri Seeds (Coriander Seeds)
Coriander seeds add warmth and depth to dishes. They can be:
-
Roasted and ground for curries, stews, and spice blends.
-
Used whole in pickles, soups, and braised vegetables.
Innovative and Global Recipes with Koriandri
| Cuisine | Recipe Example | Koriandri Part Used |
|---|---|---|
| Indian | Coriander Chutney | Leaves & Seeds |
| Mexican | Fresh Salsa | Leaves |
| Thai | Tom Yum Soup | Roots & Seeds |
| Middle Eastern | Spiced Lamb Meatballs | Seeds |
| Mediterranean | Quinoa Salad with Herbs | Leaves |
Case study: A modern chef in Mexico reports that adding fresh coriander leaves to tacos increased customer satisfaction by 30%, showing its impact on flavor and aroma.
How to Grow and Store Coriander
Growing Koriandri at Home
Koriandri thrives in well-drained soil and plenty of sunlight. Tips:
-
Sow seeds ¼ inch deep and keep the soil moist.
-
Use pots indoors if space is limited.
-
Watch for pests like aphids; neem oil is a natural deterrent.
Storing Fresh Koriandri Leaves
Fresh leaves spoil quickly. Preserve them by:
-
Place in a glass of water in the fridge, loosely covered.
-
Freeze chopped leaves in ice cube trays with a bit of water or oil.
Storing Koriandri Seeds
-
Keep seeds in airtight containers in a cool, dark place.
-
Whole seeds last up to a year; ground seeds retain flavor for 6 months.
Koriandri in Traditional Medicine and Wellness
Ayurvedic and Herbal Uses
Koriandri is considered cooling and calming in Ayurveda. It’s used to aid digestion, relieve anxiety, and detoxify the body. Coriander seed water is a traditional remedy for urinary tract health and bloating.
Modern Research on Koriandri
Recent studies support koriandri’s health claims:
-
Anti-diabetic properties of seeds.
-
Antioxidant activity of leaves.
-
Cholesterol-lowering effects in small clinical trials.
Koriandri Safety, Precautions, and Allergies
Possible Allergic Reactions
Although rare, some people may develop skin rashes, swelling, or digestive discomfort after consuming koriandri.
Safe Consumption Levels
Moderate daily use of leaves and seeds is generally safe. Excessive intake of seeds may cause digestive upset.
Interactions with Medications
Koriandri may interact with blood sugar-lowering or blood pressure medications. Consult a healthcare professional if you’re on these treatments.
FAQs About Koriandri
-
What is the difference between koriandri leaves and seeds?
Leaves are fresh and aromatic, seeds are dry and nutty-flavored. Both offer unique health benefits. -
Can coriander help with digestion?
Yes, both leaves and seeds support digestive health and relieve bloating. -
How should I store koriandri for maximum freshness?
Leaves in water or frozen, seeds in airtight containers in a dark, cool place. -
Are there any side effects of koriandri?
Rarely, allergic reactions or mild digestive discomfort may occur. -
Can coriander be used in weight loss?
It may aid digestion and metabolism, supporting weight management when combined with a healthy diet.
Conclusion
Koriandri is far more than a garnish or spice. Its leaves, seeds, and roots provide culinary richness, powerful antioxidants, and numerous health benefits. From enhancing your favorite recipes to supporting heart, digestive, and skin health, koriandri proves to be a versatile and indispensable herb. Whether you grow it at home, use it fresh in salads, or grind the seeds for your favorite dishes, coriander adds flavor, nutrition, and history to your table.
Start exploring koriandri today and discover how this humble herb can transform your meals and health naturally.