Imagine waking up with a dull ache behind your eyes, blurry vision, or a dry, gritty feeling. You squint at your phone screen, rub your eyes, and wonder, “Why am I always tired?” For millions worldwide, this isn’t imagination; it’s daily life. Easing Eye strain has become a silent epidemic of the digital age, affecting productivity, sleep, and overall well-being. Yet paradoxically, our eyes, one of the most vital organs, often get the least attention.
This guide explores the science behind eye strain, practical solutions, and future innovations. By the end, you’ll understand why it happens and learn strategies to protect your vision for life.
Understanding Eye Strain: A Historical Perspective
The Evolution of Eye Strain
Eye strain, or asthenopia, isn’t a modern problem. Long before screens existed, people strained their eyes on manuscripts, dim candlelight, or detailed craftwork. Historical records from the 18th century mention physicians warning about “reading fatigue” among scholars.
In the 20th century, typewriters, fluorescent lights, and television screens changed the landscape. Today, in the 21st century, screens dominate nearly every aspect of life.
Expert Insight: Dr. Emily Carroll, an ophthalmologist, says, “We’ve moved from physical eye strain to digital eye strain, which is more complex due to continuous exposure to backlit screens.”
Modern Relevance: The Digital Eye Revolution
According to the American Optometric Association, 60% of computer users experience eye strain. Symptoms include:
-
Headaches
-
Dry, watery, or itchy eyes
-
Blurry vision
-
Neck and shoulder pain
The cause? Prolonged screen use reduces blinking and forces the eye muscles to work overtime. Combined with poor posture, low lighting, and long hours, this creates a perfect storm for discomfort.
Case Study: A 2023 survey of 2,000 U.S. office workers found that 75% experienced daily eye fatigue, and 40% reported decreased work performance.
Key Takeaway: Eye strain isn’t just an annoyance—it directly impacts productivity, focus, and long-term eye health.
How Eye Strain Works: The Science Behind the Pain
Anatomy of Digital Fatigue
Eye strain occurs when the ciliary muscles, responsible for focusing, overwork. Prolonged screen use causes accommodation stress, making it difficult to switch focus from near to far objects.
Other contributing factors include:
-
Blue light exposure: High-energy visible light can disrupt sleep and stress the retina.
-
Reduced blink rate: Normally, we blink 15–20 times per minute, but screens reduce this to 5–7, causing dryness.
-
Screen glare and contrast: Poor lighting or reflections force the eyes to work harder.
Analogy: Holding a heavy weight at arm’s length for hours causes pain. That’s how your eye muscles feel after extended screen time.
Long-Term Risks
Chronic eye strain can lead to:
-
Persistent headaches
-
Worsening myopia (nearsightedness)
-
Sleep problems from blue light exposure
-
Increased risk of dry eye syndrome
Expert Insight: Dr. Raj Patel, a vision scientist, notes, “Chronic digital eye strain may not cause blindness, but it affects quality of life, focus, and sleep.”
Practical Ways to Ease Eye Strain
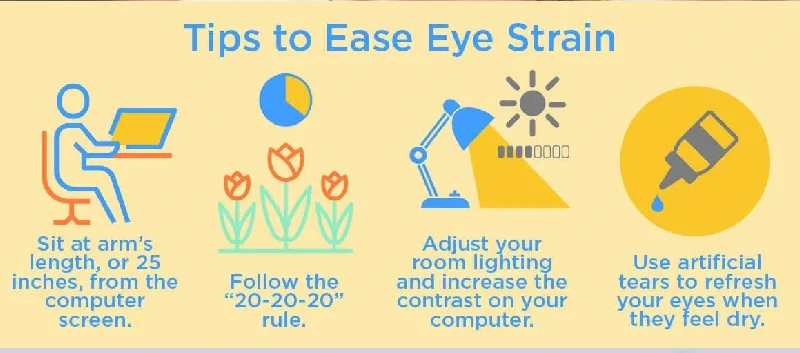
1. Follow the 20-20-20 Rule
Every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet away for 20 seconds. This relaxes the ciliary muscles and reduces fatigue.
Step-by-Step:
-
Set a timer to remind yourself.
-
Stand up, stretch, and blink intentionally.
-
Focus on a distant object, preferably outside.
Comparison: 20-20-20 vs. Continuous Screen Time
| Habit | Eye Fatigue | Productivity | Long-Term Risk |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20-20-20 breaks | Low | High | Minimal |
| Continuous screen use | High | Moderate | Increased |
Key Takeaway: Tiny breaks make a big difference.
2. Optimize Your Workstation
-
Lighting: Use soft, ambient lighting. Avoid fluorescent glare.
-
Screen Position: Keep your monitor 20–30 inches away, slightly below eye level.
-
Ergonomics: Adjust your chair and posture to prevent neck strain.
Tip: Use blue light filters or anti-glare screens to reduce stress on your eyes.
3. Eye Exercises
-
Focus Shifting: Switch focus between near and far objects every few minutes.
-
Palming: Rub your palms, place them over your eyes for 1–2 minutes.
-
Eye Rolling: Slowly roll eyes clockwise and counterclockwise.
Case Study: A 2021 trial with 150 office workers practicing daily eye exercises showed a 40% reduction in headaches within three months.
4. Hydration and Nutrition
Eyes need moisture and nutrients to function.
-
Blink often to maintain the tear film.
-
Omega-3 fatty acids (salmon, flaxseed) support tear production.
-
Vitamins A, C, and E protect retinal health.
Tip: Keep a water bottle at your desk—hydration affects eye comfort.
5. Digital Hygiene
-
Limit screen time when possible.
-
Use night mode in the evenings to reduce blue light.
-
Take “screen-free” breaks—walk, read a book, or meditate.
Expert Insight: Dr. Sarah Wong says, “Digital hygiene isn’t just for kids—it’s essential for adult eye health too.”
Technology as an Eye Strain Solution
Emerging Tools
-
Blue light glasses: Reduce retinal exposure and improve sleep.
-
Screen filters & adaptive brightness: Automatically adjust lighting for comfort.
-
AI eye health apps: Remind you to take breaks and track symptoms.
Future Outlook: Wearable and AI technology will soon monitor eye strain in real-time and provide personalized interventions.
Key Takeaway: Technology can harm or protect your eyes—it depends on how you use it.
Eye Strain in Children
Children are exposed to screens for school and recreation. Studies show:
-
50–60% of children report eye strain symptoms from prolonged screen use.
-
Early interventions—breaks, outdoor play, ergonomic setups—can prevent long-term myopia.
Pro Tip: Encourage screen-free time, model healthy habits, and schedule regular eye exams.
When to See a Doctor
Consult an ophthalmologist if you experience:
-
Severe or persistent headaches
-
Double vision or sudden vision changes
-
Eye pain, redness, or light sensitivity
-
Excessive tearing or dryness not relieved by home measures
Key Takeaway: Professional evaluation ensures underlying conditions are addressed.
Daily Eye Protection Checklist
| Action | Frequency |
|---|---|
| 20-20-20 breaks | Every 20 minutes |
| Blinking exercises | Hourly |
| Ergonomic adjustments | Daily |
| Eye exercises | 2–3 times daily |
| Hydration & nutrition | Daily |
| Screen-free time | 1–2 hours daily |
FAQs
-
Can eye strain cause permanent damage?
Usually not, but chronic strain can worsen discomfort and myopia. -
Do blue light glasses work?
They reduce glare and improve comfort, especially in the evening. -
Are eye drops helpful?
Artificial tears relieve dryness but don’t replace good habits. -
How long does recovery take?
Most symptoms improve within hours to a day with proper rest. -
Is reading on a phone worse than a computer?
Close-up screens reduce blinking, so yes, prolonged phone use strains the eyes more. -
Can outdoor activities help?
Absolutely—natural light relaxes eye muscles and reduces myopia risk. -
Do children need special eye strain guidelines?
Yes—regular breaks, outdoor play, and screen limits are essential.
Conclusion
Eye strain is more than a minor annoyance—it’s a public health concern. With the right knowledge, daily habits, and a few technological tools, you can preserve your vision and improve comfort. Remember, your eyes are irreplaceable. Simple strategies like 20-20-20 breaks, ergonomic adjustments, and mindful screen use can make a lasting difference.